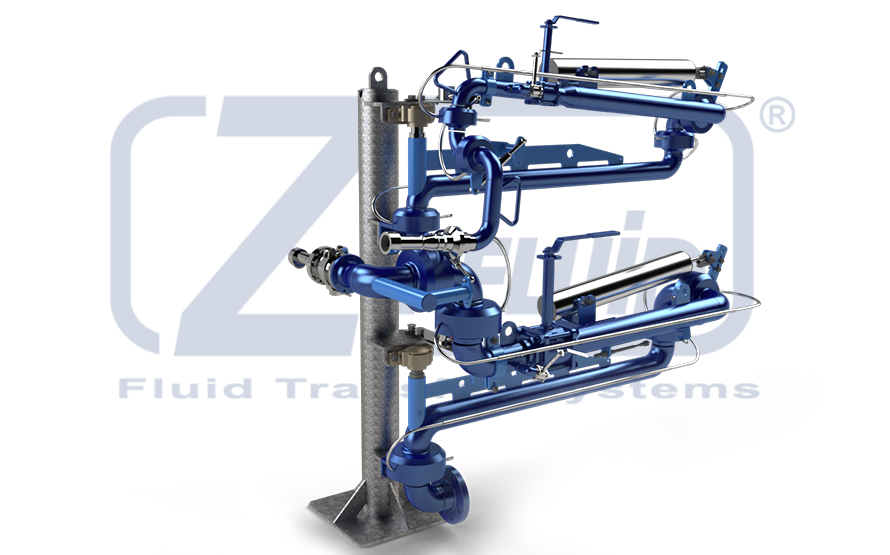
LNG (liquified natural gas) is obtained from natural gas (NG) through specific purification and dehydration treatments. The gas is then cooled down until it is condensed to liquid.
The process of liquefaction reduces the specific volume of gas by about 600 times when compared to the standard conditions, it allows the storage and transportation of a considerable quantity of energy in extremely reduced space at relatively reduced costs.
LNG is transported on long distances from the production place to destination by sea on special ships, where it is stored mostly in its liquid form at atmospheric pressure and cryogenic temperatures (around -160 °C).




